Lesson 01: Hello World
Create Your First C/C++ Console Program
Objective
- Learn how to create a console project in Visual C++ or C++Builder IDE
Software Requirement
- Visual C++ 2017 or newer edition
- Or C++ Builder 12.x or newer edition
- Or XCode in Mac OS X system
Overview
There are two types of C/C++ compilers, each of which has advantages and disadvantages:
- Command-line C compilers
- IDE (Integrated Development Environment) or Windows C/C++ compilers
Command-Line C Compilers
If you use a command-line C compiler to compile and execute a C program, you have to go through the following steps:
- Write the C code in a text editor or word processor.
- Save the file as
myfile.cfile in your C project folder. - Compile the code to a computer-executable program by entering a compiler command at a command prompt or console window.
For GUN C compiler:gcc -Wall -o myfile myfile.c
For Microsoft Visual C++ command-line compiler:cl myfile.c
For C++Builder compiler:bcc32 myfile.c - Execute the program by entering
myfile
At the command prompt. Then, you should see the program's results on the screen.
You can use any text editor or code editor that you prefer using with the command-line C compiler. Here are some helpful text editors that most programmers are like:
IDE C/C++ Compilers
An Integrated Development Environment, or IDE for short, is an application or software that programmers use. It helps a programmer program quickly by providing all the comprehensive facilities required for software development. IDE can improve a programmer's or developer's productivity because of its fast setup and various tools. Without this, a programmer takes a lot of time deciding on various tools for their tasks.
Mainly, an IDE includes 3 parts: source code editor, build automation tool (compiler), and debugger. The source code editor is something where programmers can write the code. In contrast, the programmers use the build automation tool to compile the codes, and the debugger is used to test or debug the program to resolve any errors in the code. Furthermore, these IDEs also come with additional features like object and data modeling, unit testing, source code library, and more.
Currently, several IDEs are available for various programming languages like Python, C++, and Java. JavaScript, R, and others. Modern IDEs even possess intelligent code completion to maximize the programmer's productivity.
- The IDE compilers usually have a built-in code editor colorized for C/C++. That means the C/C++ keywords are in one color (like blue), text in text strings may be in another color (like red), comments may be in green, and other text is in black. And if you misspell a keyword in C/C++ or miss a quotation mark, this becomes immediately obvious.
- It takes less time and effort. It includes various tools and features that help prevent mistakes, organize resources, and provide shortcuts.
- It allows quick navigation to the type.
- Programmers can quickly navigate to other members by using hyperlinks.
- IDEs organize imports and can add appropriate imports.
- It can give a warning in case of any errors or mistakes.
- IDEs are great for generating or completing the code depending on previous codes.
- These environments make the unit tests run quickly.
- Commercial IDE C/C++ compilers cost money.
- Usually, you must install it on your computer, and more disk space is required to install the software.
- Using a command-line compiler is much faster than an IDE.
- In a UNIX/Linux computer system, you can not operate the IDE over the telnet interface.
Lab Experiment
Now, you will learn how to create a new project for a Windows console application in the IDE
Microsoft Visual C++ 2019
Before writing any C code, you must create a folder to store all the C projects. On the Windows desktop, create a folder named EE2450.
If you are the first time to launch the Visual Studio, please read this...
When you launch Visual Studio 2019 (VS2019) for the first time, the VS2019 will ask you to sign in, create an account, or skip it. If you have a Windows account, you can sign in. Otherwise, click Not row, maybe later.
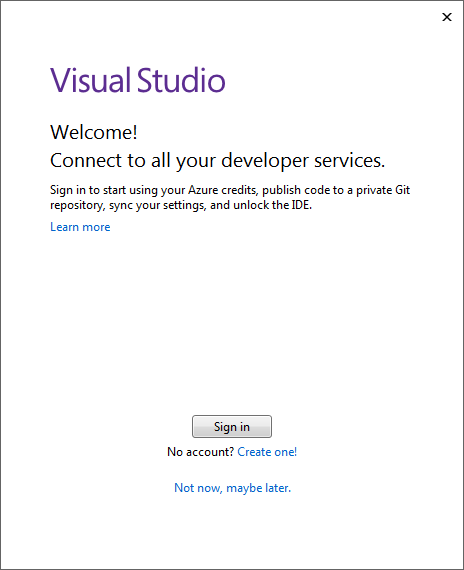
Figure 1-1: Visual Studio Welcome Window
Next, the VS2019 will ask you to select the development settings. From the combo box list, select the Visual C++ item and choose your color theme. Then click Start Visual Studio.
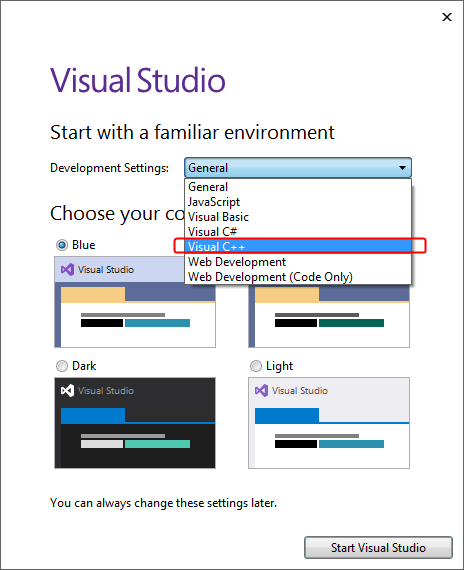
Figure 1-2: Development Environment Settings
After you launch the Visual Studio, you will see the Get Started dialog. You can click Open a project or solution to open the existing project, click Create a new project, or click Continue without code to enter the main window.
Let us create a new project for a console application.
- You can click Create a new project in the Get Started dialog or select File ➤ New ➤ Project... from the main menu in the main window.
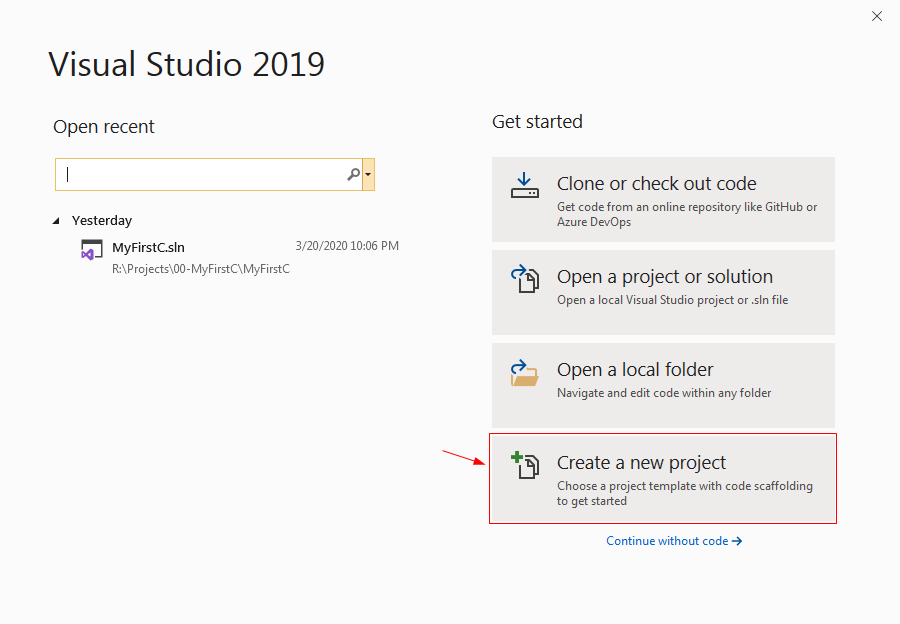
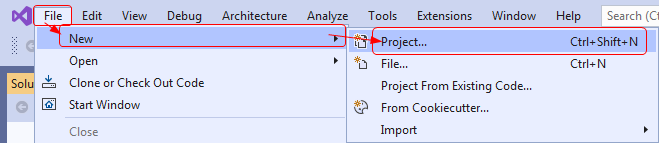
- In the Create a new project dialog, search and select
 (C++, Windows, and Console) to create a console application.
(C++, Windows, and Console) to create a console application.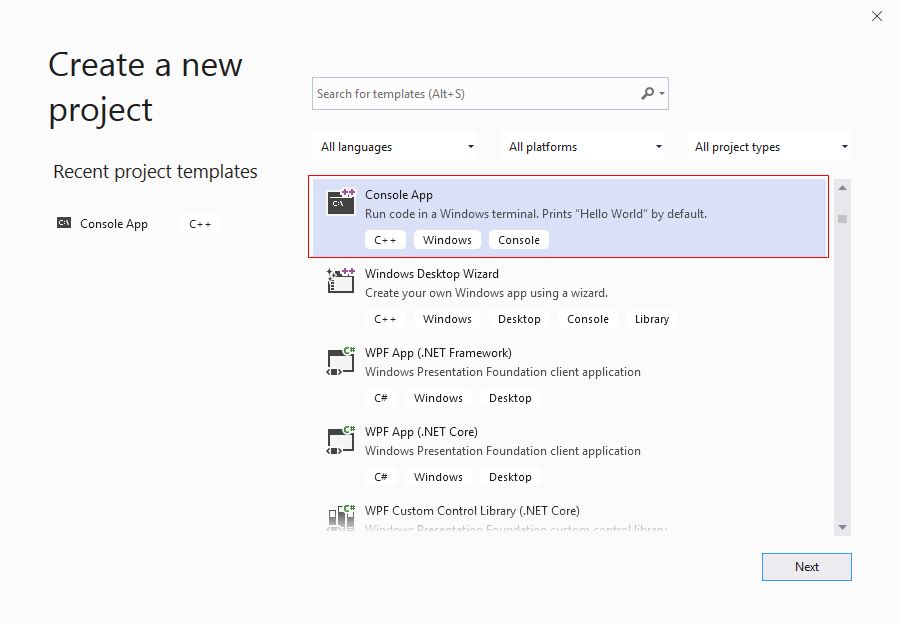
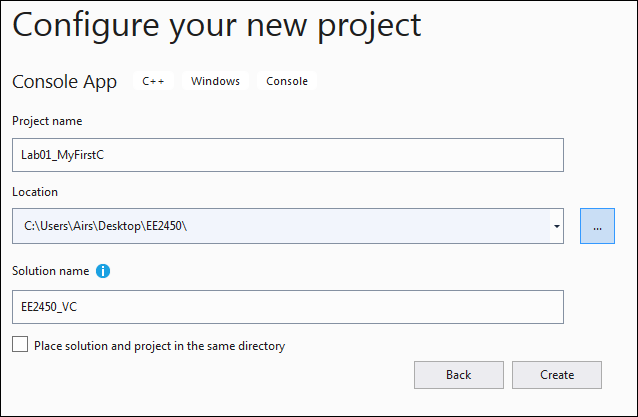
- The Configure your new project dialog will show on the screen.
- Provide a name for your project in the Project name field — for example, Lab01_MyFirstC.
- Change the project folder in the Location field: <Desktop>\EE2450\
- A solution is a container that can have one or more projects. For example, type EE2450_VC in the Solution name field.
- Do not select Place solution and project in the same directory.
- Then, the Visual Studio main window will show on the screen as below.
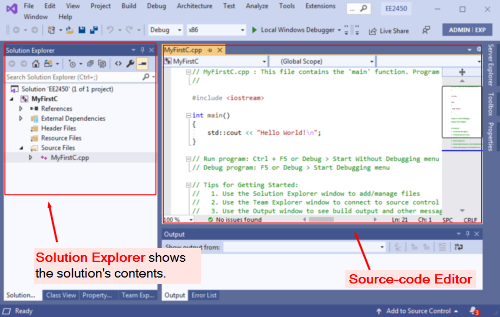
- In the Source-Code editor window, VS will automatically create a template source file, and the filename will be the same as the project name. If your VS does not create the source file, you have to add a new file into the solution by the following steps:
- In the Solution Explorer window, right-click on your Solution and select Add ➤ New Item ....
- Select C++ File (.cpp) under Installed ➤ Visual C++ catalog in the New File dialog.
- Enter main.cpp in the Name field, then click Add.
- The Solution Explorer can let you view and manage your application's files. If the Solution Explorer is not displayed, you can display it by selecting View ➤ Solution Explorer from the main menu.
- In the Source-Code editor window, VS will automatically create a template source file, and the filename will be the same as the project name. If your VS does not create the source file, you have to add a new file into the solution by the following steps:
- Enter the following code to the c source file. (you may either use the existing stub code or delete all and start from scratch)

- Compiler the code
In the main menu, select Build ➤ Build Solution to compile the code.
- Check the message in the Output window.
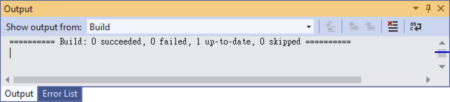
If there are any errors in your code, the Output window will show you how many failed in the code, and all the errors will be listed in the Error List window. Try to understand the error message, then double-click on the error message, the VS will point to the line of the code and then you have to fix the error.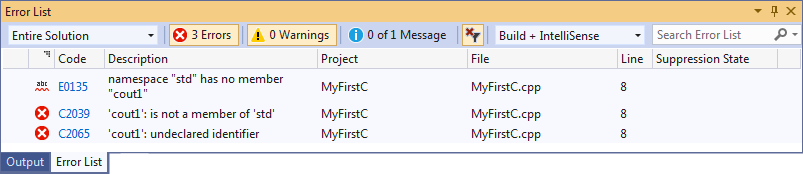
If you got error code C4996, the solutions are listed at the end of this article. - If the code can be successfully built, you can execute the program in two ways:
- Select Debug ➤ Start Debugging from the main menu, or press F5 key. The program will be launched and stop at the line where a breakpoint sets it.
- Select Debug ➤ Start Without Debugging from the main menu, or press the Ctrl+F5 key. The IDE opens a Command Prompt window and executes the program.
When you compile the code, you may get an error message: "This function or variable may be unsafe. Consider using xxxxx_s instead. To disable deprecation, use _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS." The function or variable is a pointer, and the Visual Studio compiler marks it as unsafe. You can modify the code to use the Microsoft-invented functions suggested by the compiler, but you will lose compatibility with other compilers or platforms. For code compatibility, you must disable security checks in Visual Studio. To solve this problem, you can use one of the following methods:
1. Using #define Statement
Using #define Statement
Add the following statement at the top of the source code:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <time.h>
2. Set Definition in Project Properties
Set Definition in Project Properties
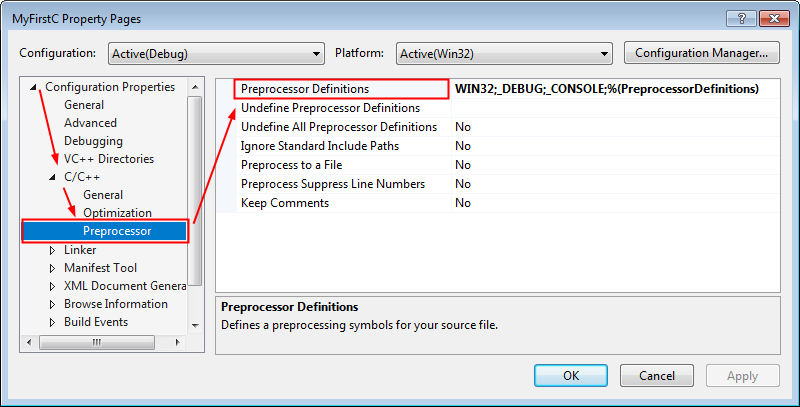
Or set the _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS definition to the Preprocessor Definitions in the project properties.
- From the main menu, select Project ➤ <project name> Properties.
- Then, in the pop-up Property Pages dialog box, select Configuration Properties ➤ C/C++ ➤ Preprocessor.
- Edit Preprocessor Definitions and add _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS last empty line.
3. Disable the Error Code
Disable the Error Code
Or you can add the following statement in the code to disable the error code.
#pragma warning(disable : 4996) // disable error code: C4996
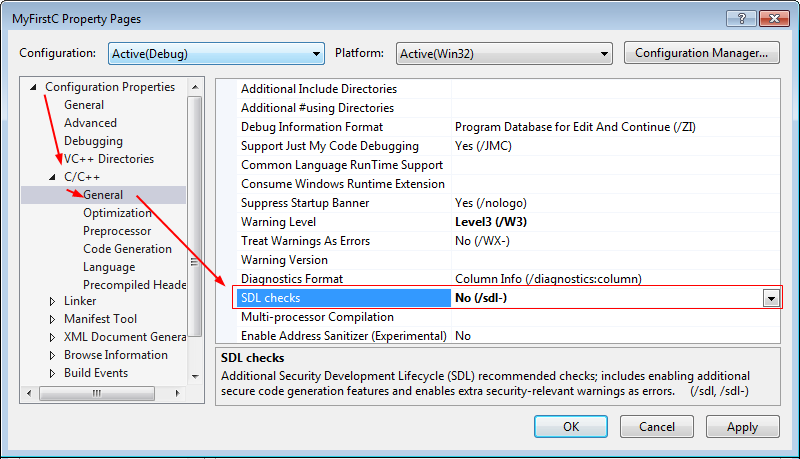
4. Disable the SDL Checks
Disable the SDL Checks
Or disable the SDL (Security Development Lifecycle) checks on the project property.
- From the main menu, select Project ➤ <project name> Properties.
- Then, in the pop-up Property Pages dialog box, select Configuration Properties ➤ C/C++ ➤ General.
- Set SDL checks to No (/sdl-)
C++Builder 12
C++Builder is a rapid application development (RAD) environment initially developed by Borland and, as of 2009, owned by Embarcadero Technologies. It includes tools that allow drag-and-drop visual development, making programming easier by incorporating a WYSIWYG graphical user interface builder.
Before writing any C code, you must create a folder to store all the C projects.
- On the Windows desktop, create a folder named EE2450.
- Double-click the EE2450 folder and create a subfolder named BCB.
- Under the BCB folder, create a subfolder named Lab01_MyFirstConsoleCpp to store the project for this lab.
The following steps show how to create a new C/C++ console application in C++Builder.
- Launch C++Builder by double-clicking
 C++Builder icon.
C++Builder icon. - From the main menu, select File ➤ New ➤ Console Application - C++Builder.
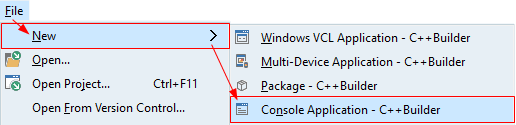
Or select File ➤ New ➤ Other... ➤ C++Builder Projects, then select Console Application in the New Items dialog box.
Console Application in the New Items dialog box.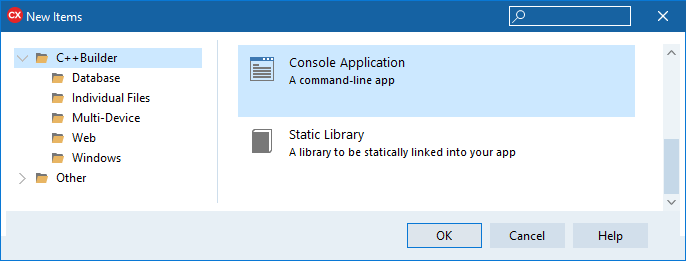
- The New Console Application dialog box opens. Select the source type (C or C++) for the main module of the project, or enable Specify project source and specify the preexisting file that contains a main() or winmain() function.
For C++, in the Target Framework group, specify the application type if you want your application to display visuals:- FireMonkey: to create a FireMonkey application
- Visual Component Library: to create a VCL application
- None: a default framework
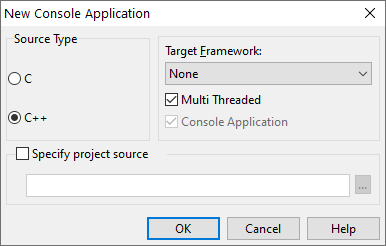
Click OK. - Then, the IDE creates a project file for this source file and displays the Code Editor.
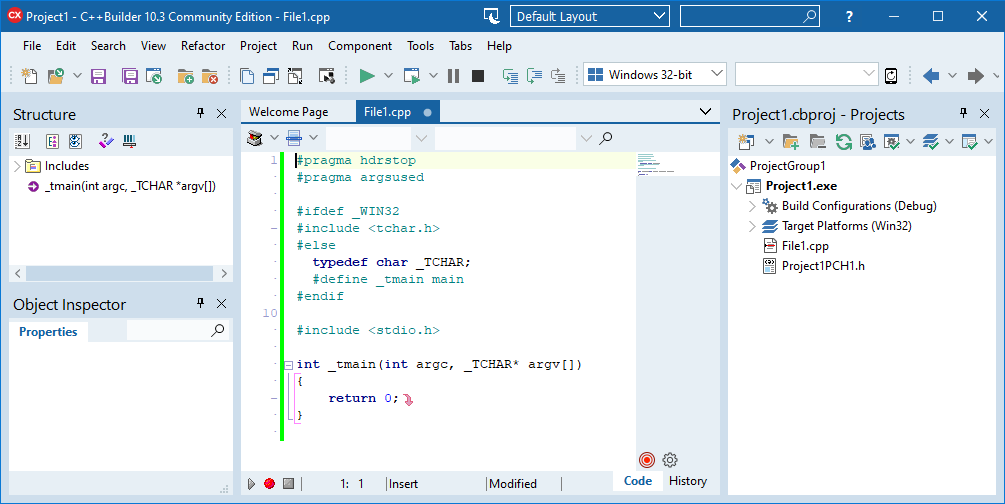
- Enter your code into the code editor (you may either use the existing stub code or delete all and start from scratch)
#include iostream #include tchar.h #include time.h using namespace std; int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { time_t currTime = time(NULL); cout << "Hello, welcome to the C++ world!!" << endl << endl; if (currTime != (time_t) (-1)) { cout << "The current local time is " << asctime(localtime(&currTime)) << endl; } cout << endl << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - Project Saving
Before the beginning of the application development is recommended to save the project by selecting File ➤ Save All from the main menu or clicking the Save All button from the toolbar.
Save All button from the toolbar.
Saving a project takes place in four steps.- The first step is to save the project file. Change the filename to 01_MyFirstConsoleCpp.cbproj and click Save.
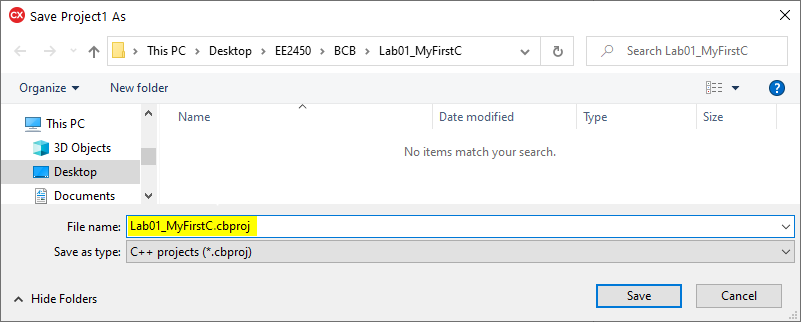
- The second step is to save the main file. By default, the filename is proposed as File1.cpp. Browse to the project folder and change the file name to main.cpp, then click Save.
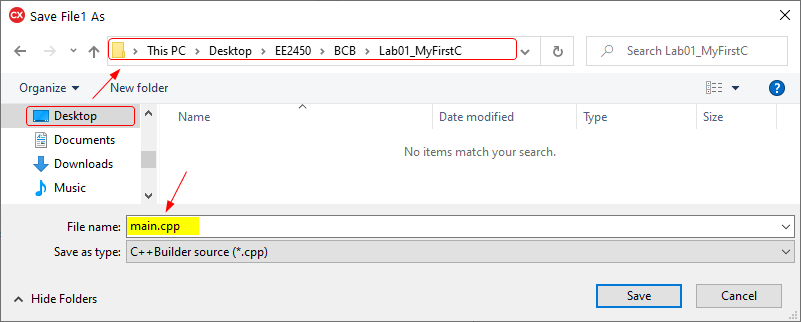
- The last step is saving the project group file. In the Projects window, right-click on the ProjectGroup1 and select Save Project Group.
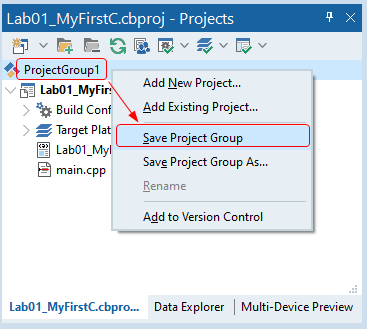
Then change the folder to Desktop ➤ EE2450 ➤ BCB, change the filename to EE2450_BCB.griupproj, and click Save.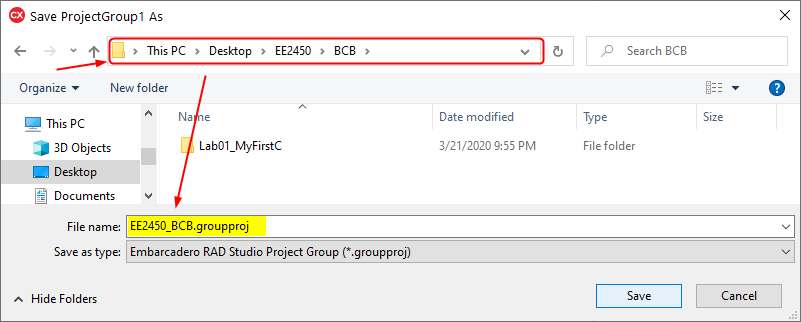
- The first step is to save the project file. Change the filename to 01_MyFirstConsoleCpp.cbproj and click Save.
- Compile the code
In the main menu, select Project ➤ Build 01_MyFirstConsoleCpp to compile the code, or press the Shift+F9 key to build the code.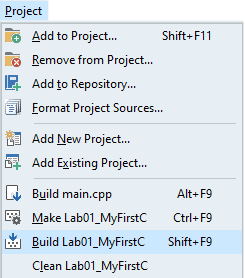
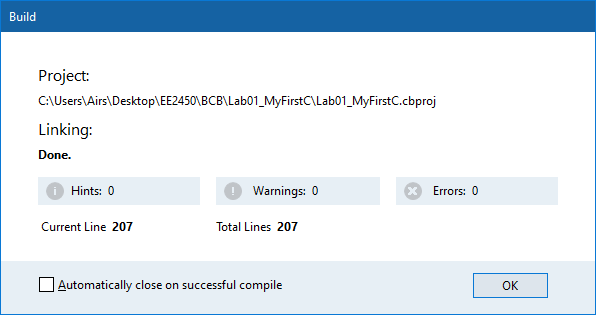
If there are any errors in your code, the Build dialog will show you how many errors are in the code, and all the errors will be listed in the Messages window. Try to understand the error message, then double-click on the error message, the IDE will point to the line of the code and then you have to fix the error. - If the code can be successfully built, you can execute the program in two ways:
- Select Run ➤ Run from the main menu, click the
 Run button, or press the F9 key. The program will be launched and stop at the line where a breakpoint sets it.
Run button, or press the F9 key. The program will be launched and stop at the line where a breakpoint sets it. - Select Run ➤ Run Without Debugging from the main menu, click the
 Run Without Debugging button, or press the Control + Shift + F9 key. The IDE opens a Command Prompt window and executes the program.
Run Without Debugging button, or press the Control + Shift + F9 key. The IDE opens a Command Prompt window and executes the program.
- Select Run ➤ Run from the main menu, click the
What is the difference between Compile, Build, and Make in the Project Build menu?
As you develop your application in the IDE, you can compile (or make), build, and run the application in the IDE. All three operations can produce an executable (such as .exe, .dll, .obj, or .bpl). However, the three operations differ slightly in behavior:
- Compile (Project ➤ Compile) or, for C++, Make (Project ➤ Make) compiles only those files that have changed since the last build and any files that depend on them. Compiling or making does not execute the application (see Run).
- Build (Project ➤ Build) compiles all of the source code in the current project, regardless of whether any source code has changed. The building is useful when unsure which files have changed or if you have changed project or compiler options.
- Run (Run ➤ Run (F9)) compiles any changed source code and executes your application if the compile is successful, allowing you to use and test it in the IDE.
Run the code and capture the screen. Paste it to your report.
Extra Useful Information for You!
How to capture your screen in Windows 11?
How to capture your screen in Windows 11?
There are many ways to take screenshots on Windows. Windows 11 has several built-in screenshot tools and some excellent free options if you want more features.
Windows 11
On Windows 10, you can just press Windows + PrtScn on your keyboard to instantly save a full-screen screenshot in PNG form to your Pictures folder.
You can also press the PrtScn key on any version of Windows to save a copy of your screen (or Alt + PrtScn for just the active window) to your clipboard. You can then paste it into any application. On Windows 10, you can press Windows + Shift + S to capture a region of your screen and copy it to your clipboard.
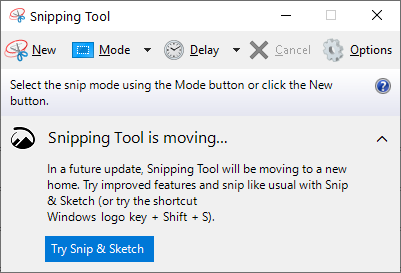
If you want something more powerful, you can launch the Snipping Tool, which is included with Windows 7, 8, and 10. To find the Snipping Tool, click the  Start button and type snip. The
Start button and type snip. The ![]() Snipping Tools can take screenshots of your full screen, a single window, or an area of your screen. You can set a delay of up to five seconds if you need time to set up a screenshot after clicking the button.
Snipping Tools can take screenshots of your full screen, a single window, or an area of your screen. You can set a delay of up to five seconds if you need time to set up a screenshot after clicking the button.