Tiva Lab 04: LED Dice
Objective
- To design and program an electrical LED dice using a microcontroller and 7 LEDs
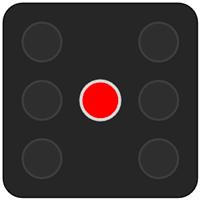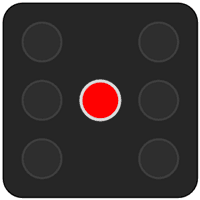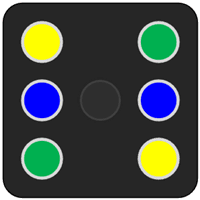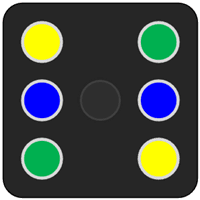
Design and write the program in the embedded system that generates a random number between 1 and 6 (inclusive) when a push button is pressed, and displays the corresponding number of dots on the 7 LEDs for 2 seconds. You can use a pseudo-random number generator and a switch-case statement to map the numbers to the LEDs. For example, 1 can be shown as the center dot, 2 as the opposite dots, 3 as a diagonal line, 4 as a square, 5 as a cross, and 6 as a hexagon. You may also add other features like sound, animation, or delay to enhance the user experience.
Required Reading Materials
- Lesson 07: Create an ARM C Application with Keil μVision MDK-ARM
- Lesson 09: GPIO Ports and Configurations
- Set, Clear, Toggle, and Check Bit Value in C
- Polling Method in Embedded Programming
Components Required
- Microcontroller board (such as PSoC board, TI TIVA board, or similar)
- Breadboard and jumper wires
- 7 LEDs (2 yellows, 2 green LEDs, 2 blue LEDs, and one red LED)
- 11 220-ohm resistors
- An L293 TTL Chip (Datasheet)
| Component/Device | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| 220 Ω (red red brn gld / red red blk blk brn) | × 11 | |
| Red LED | × 1 | |
| Green LED | × 2 | |
| Blue LED | × 2 | |
| Yellow LED | × 2 | |
| L293D Quadruple Half-H Drivers | × 1 |
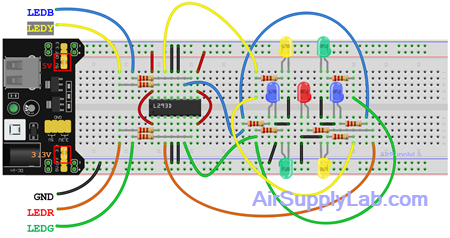
Circuit Diagram
- Insert the 7 LEDs on the breadboard to form a dice diagram, as shown above. Connect each LED to a 220-ohm resistor. The resistors limit the current flowing through the LEDs and protect them from damage due to overcurrent.
- Connect each LED-resistor pair to an output pin of the L293D chip, as shown in the diagram.
- Connect pins LEDR, LEDG, LEDB, and LEDY to the microcontroller. Ensure that these pins are set to output mode in the program.
Safety Tips:
- Do not connect the LEDs directly to the digital pins without resistors.
- Disconnect the power cable (including the USB on the microcontroller board) before making any changes to the circuit.
Pin configurations
| Device | Port.Pin | Signal Type | Module | Direction | Drive Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Procedure
- Start a new project in your IDE and create a folder named "003_LED_Dice".
- Include the necessary header files.
- Define the pins for 4 pairs of LEDs and a push button. Ensure that the LEDs' pins are set to output mode and the pin for the button is set to input mode with a pull-up or pull-down resistor.
- Start with the dice displaying a value of 1
- Increment the displayed dice value to the next value. After reaching 6, reset to 0.
- If the push button (SW1) is pressed, display the dice value every 100ms.
- If the button is released, display the dice value every 200 ms for a duration of (1000 + random value) ms. The random value should range from 100 to 1000.
- Continuously check if the button is pressed again and repeat steps 5 to 7 accordingly.
Programming Tips:
- To detect the state of SW1, consider using software edge detection methods that trigger an action when the button's state changes from pressed to released or vice versa. For example:
- When SW1 is pressed, new dice values are displayed every 100 ms.
- When SW1 is released, display new dice values every 200 ms for 1 ~ 3 seconds (1000 ms + a random value), then stop.
typedef enum DICE_LED{
_LEDR,
_LEDG,
_LEDY,
_LEDB
} DICE_LED;
DICE_LED dice[] = {
_LEDR, // for dice value 1
_LEDY, // for dice value 2
_LEDR | _LEDY, // for dice value 3
_LEDY | _LEDG, // for dice value 4
_LEDY | _LEDG | _LEDR, // for dice value 5
_LEDY | _LEDG | _LEDB // for dice value 6
};